AVM explains band steering
AVM Content
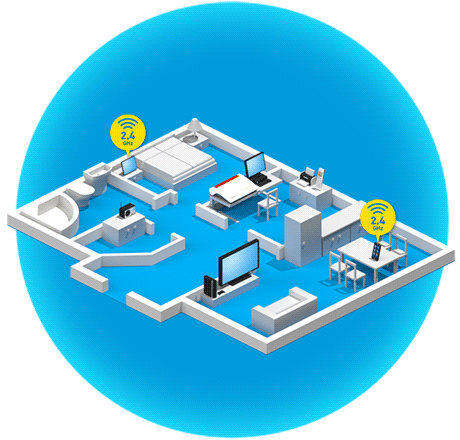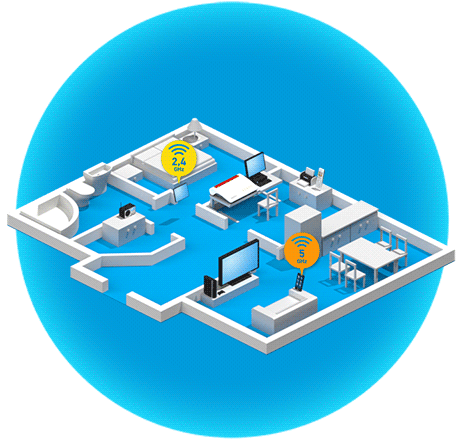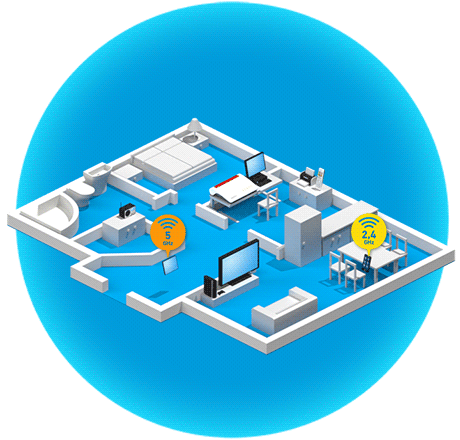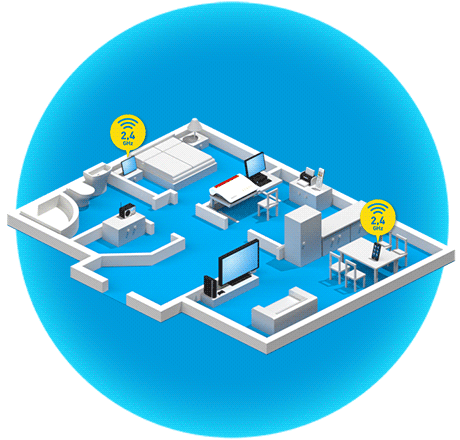
What is band steering?
Band steering technology takes the idea of dual Wi-Fi a step further. Many devices like smartphones, tablets and notebooks already support the alternative use of two Wi-Fi bands. In this scenario the devices reciprocally support both the 2.4 GHz and the 5 GHz Wi-Fi bands and – if needed – can continue data transmission on the band that is less loaded. Especially when switching to the 5 GHz band, which usually experiences less traffic, Wi-Fi performance is noticeably improved.
Band steering designates the process in which the FRITZ!Box takes over band management automatically, deciding itself which dual band device uses which band. This way devices are integrated far more efficiently in the Wi-Fi network, as apparent in the improved data transmission rate.
What are the differences between the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands?
|
5 GHz |
2.4 GHz |
|
|
Range |
very good short-range coverage |
especially good coverage even over greater distances |
|
Data throughput |
very high |
high |
|
Free of interference |
especially robust |
less robust |
|
Client support |
only recent wireless devices |
all wireless devices |
|
Channels avoiding overlapping |
up to 23 |
max. 3 |
|
Ideal for: |
media streaming, downloads |
surfing, email traffic |

What are the requirements?
- The wireless device must be capable of dual band (2.4 and 5 GHz bands must be supported, see documentation of the wireless device).
- The FRITZ!Box must use the same SSID (name of the radio network) for 2.4 and 5 GHz (this is preconfigured in the factory settings of the FRITZ!Box).
- The FRITZ!Box must support Wi-Fi 5.
- The FRITZ!Box must have FRITZ!OS 6.80 or higher installed.
In this guide you can see what else you can do to improve Wi-Fi performance.












 Deutschland
Deutschland International (English)
International (English) België (Nederlands)
België (Nederlands) Luxemburg (Deutsch)
Luxemburg (Deutsch)