AVM explains Mesh Wi-Fi steering
AVM Content
Mesh Wi-Fi steering is at the forefront of the latest FRITZ!OS developments. With the help of Mesh Wi-Fi steering, the Mesh Master (FRITZ!Box) automatically steers the wireless devices to the wireless access point with the best Wi-Fi reception and at the same time to the most suitable frequency band. In the following article we'll explain how you can benefit from Mesh steering.
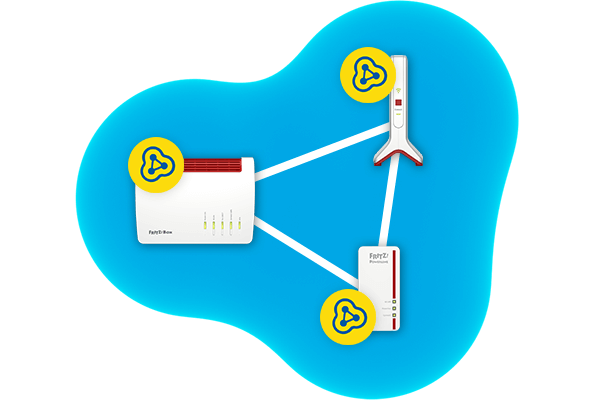
What is Mesh Wi-Fi steering?
In the Mesh, the FRITZ!Box in its function as Mesh Master has connection information of all terminal devices with Wi-Fi capability (e.g. smartphones or laptops) and all Mesh Repeaters (e.g. another FRITZ!Box, a FRITZ!Repeater or a FRITZ!Powerline adapter), which are also referred to as "access points" – or "AP" for short. As soon as the Mesh Master determines that an optimum connection is available for a wireless device, it prompts the device to change to a more suitable Mesh Repeater or to another frequency band network.
Mesh Wi-Fi steering works even more intelligently with the latest FRITZ!OS. Other aspects are taken into account in the steering decision, including the type of connection and the speed and utilization of the various possible connection routes.
In contrast to Wi-Fi roaming, with Mesh Wi-Fi steering it's the Mesh Master that decides when it makes sense to switch to a different network, and not the wireless device itself. This has the crucial advantage that the Mesh Master can better judge which wireless access point or which frequency band is ideal at any given moment as it has information about all of the wireless devices and their connections, including how much the Mesh Repeaters are being used.
For Mesh Wi-Fi steering to take effect, all wireless devices must fully support the 802.11k and 802.11v Wi-Fi standards. However, the decision as to whether the Mesh Master's request to switch is also carried out always lies with the wireless device itself.
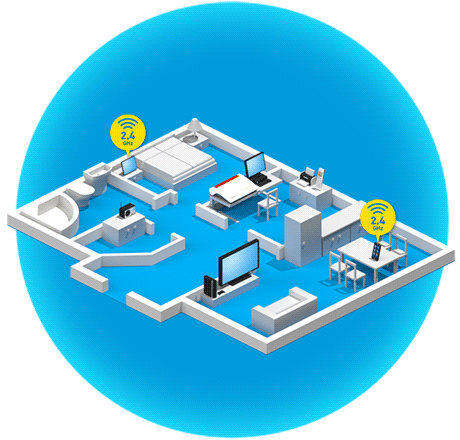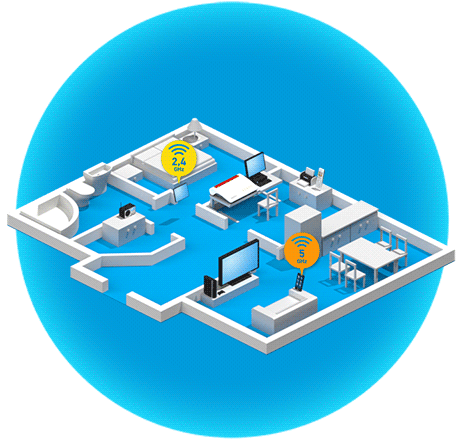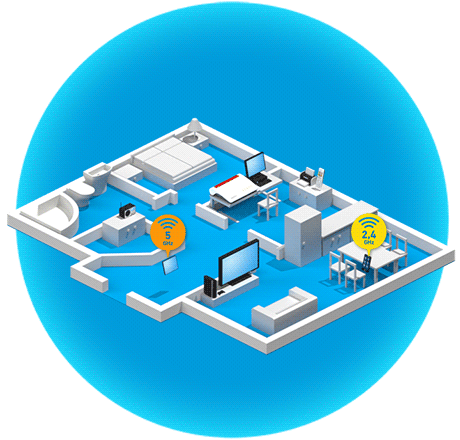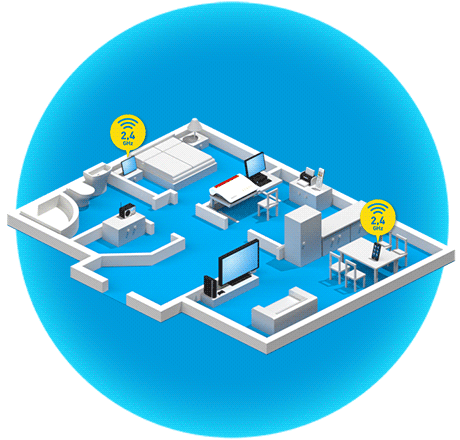
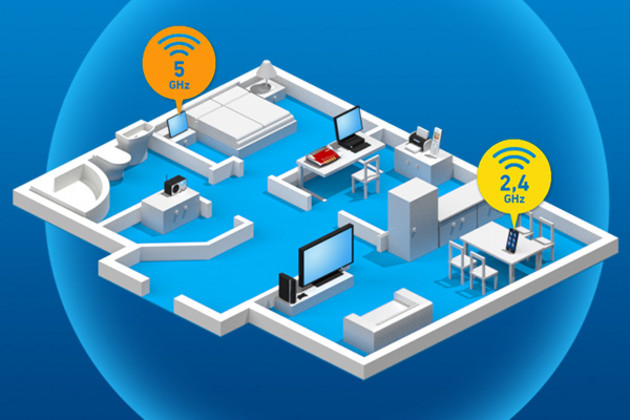
What are the benefits of band steering?
Band steering technology takes the idea of dual Wi-Fi (2.4 and 5 GHz bands) a step further. Many modern wireless devices already support the alternative use of two Wi-Fi bands. Band steering refers to the process in which the FRITZ!Box automatically takes over this band management. The Mesh Master automatically decides which frequency band a wireless device uses to connect to a FRITZ!Box, FRITZ!Repeater or FRITZ!Powerline adapter. This ensures that the wireless device is always automatically connected via the frequency band that gives it the best data throughput with the greatest possible stability in the current moment.
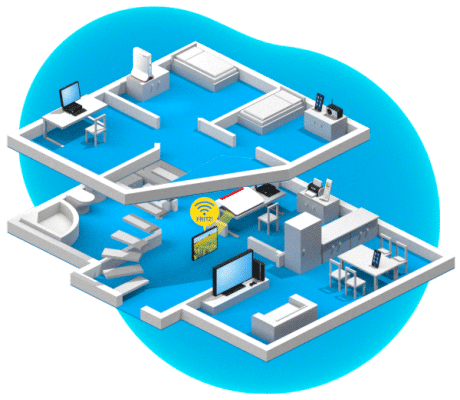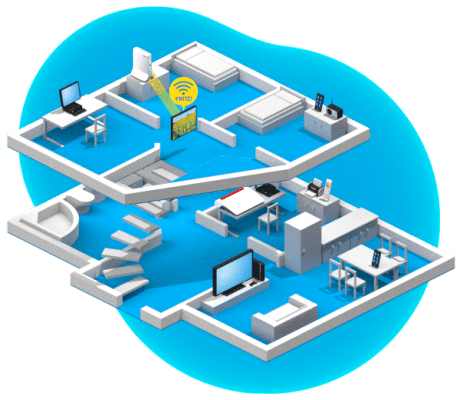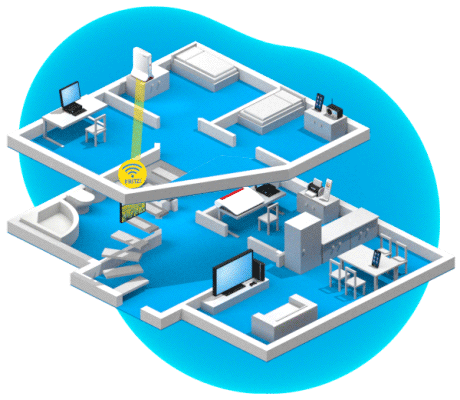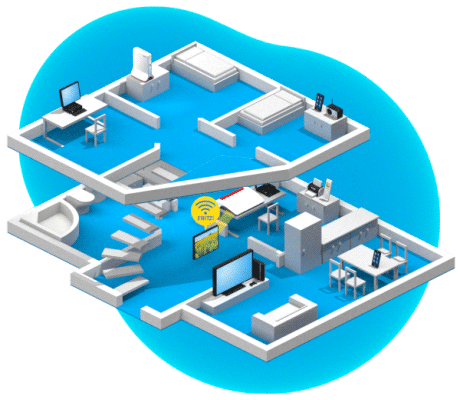
Optimization thanks to AP steering
AP steering is used to control which Mesh Repeater (the access point) a wireless device uses to connect to the home network. The Mesh Master (FRITZ!Box) constantly analyzes all Wi-Fi connections in the home network. As soon as it determines that a wireless device could establish a significantly better connection via a different wireless access point, it prompts the device to switch to a different Wi-Fi network. The central coordination enables the wireless device to make a seamless transition and thus an uninterrupted switch.
Four important points for Mesh steering
- You should always have the latest available FRITZ!OS version installed.
- All FRITZ! products must be integrated in the Mesh (look out for the Mesh symbol).
- All wireless devices must support the 802.11k and 802.11v wireless standards.
- The Wi-Fi network names (SSIDs) of the Mesh Master's and Mesh Repeater's frequency bands (2.4 and 5 GHz) must be identical.
In this guide you can see what else you can do to improve Wi-Fi performance.












 Deutschland
Deutschland International (English)
International (English) België (Nederlands)
België (Nederlands) Luxemburg (Deutsch)
Luxemburg (Deutsch)