FRITZ!Box for fiber optic connections
AVM Content
Fiber optic technology, with transmission speeds of several gigabits per second, is generally considered the ultimate solution when it comes to broadband connections. There are a few different fiber optic technologies – fiber optic networks with AON (point-to-point) or GPON (point-to-multipoint) are the most common. For both variants you can find a compatible FRITZ!Box.
Active Optical Network (AON): point-to-point

AON is structured according to the "point-to-point" system. Each user has their "own line" to the network operator – the cabling forms a graph with the topology of a star. This is good news for the households and businesses on the connection, as they can enjoy full bandwidth without interference or transmission loss. It is called "active" because the next network element is an "active" one from the point of view of the connection – namely the switch on the provider's side where the fiber optic line is terminated.
Passive Optical Network (PON): point-to-multipoint
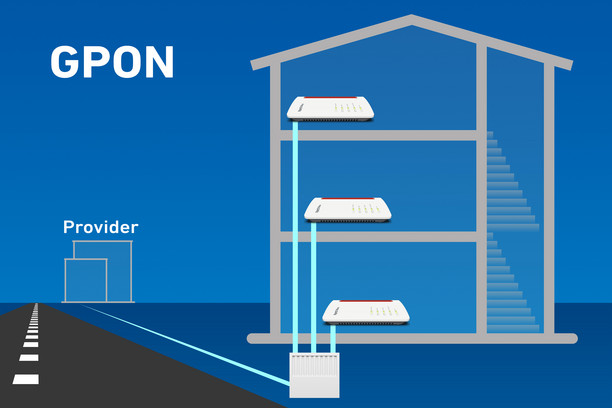
1. Gigabit Passive Optical Network (GPON)
In a PON optical network, the network operator uses simple, passive components such as optical splitters. The data transmitted by the cables of several end consumers is combined by the passive splitter and then transmitted on the same line to the network provider: point-to-multipoint. That means they're all on one single optical fiber. This makes the PON fiber optic network, like the cable network (DOCSIS) or mobile network, a shared medium. Several participants share the available spectrum.
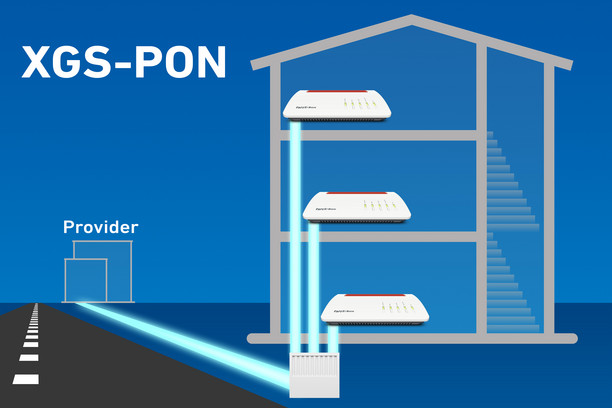
2. 10 Gigabit Symmetric Passive Optical Network (XGS-PON)
XGS-PON is an updated standard of GPON. PON fiber optic networks are defined in various standards, with one of the differences being the maximum bandwidth. With XGS-PON, data rates of up to 10 Gbit/s can be achieved both downstream and upstream, making it significantly more broadband than its predecessor.
How fast is fiber optics?
Fiber optic connections currently allow data rates of up to 10 Gbit/s, although a typical fiber´optic connection for residential customers in Germany is usually offered at 1 Gbit/s. However, fiber optic networks have a very high expansion potential, which is why higher data rates can also be offered in the future.
- AON
1 Gbit/s (downstream) and 1 Gbit/s (upstream) - GPON
2.5 Gbit/s (downstream) and 1.25 Gbit/s (upstream) - XGS-PON
10 Gbit/s (downstream) and 10 Gbit/s (upstream)
What the two fiber optic technologies have in common is that the FRITZ!Box 5590 Fiber and FRITZ!Box 5530 Fiber are the suitable FRITZ!Box models.
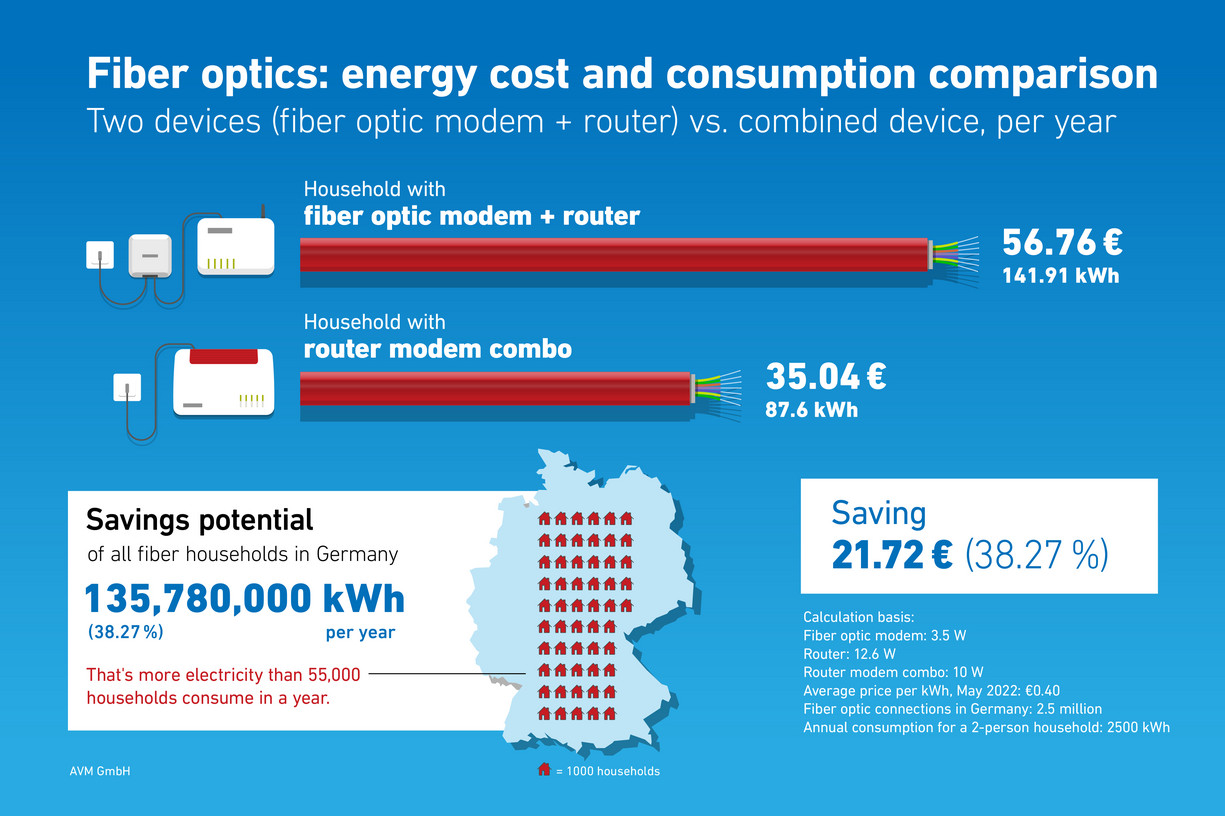
Use less electricity and save money
The advantage of a FRITZ!Box Fiber: There is no need to connect a second device to the internet. Compared to the average power consumption of a router with an external fiber optic modem, you can save around 40 percent in energy costs with a fully integrated FRITZ!Box Fiber.
Check out this guide article for a general overview of fiber optic connection types, while the infographic below shows the facts regarding electricity costs at a glance.