Knowledge Base
AVM Content
- FRITZ!Box 7690
- FRITZ!Box 7682
- FRITZ!Box 7590 AX
- FRITZ!Box 7583 VDSL
- FRITZ!Box 7583
- FRITZ!Box 7582
- FRITZ!Box 7581
- FRITZ!Box 7560
- FRITZ!Box 7530 AX
- FRITZ!Box 7530
- FRITZ!Box 7520
- FRITZ!Box 7490
- FRITZ!Box 6890 LTE
- FRITZ!Box 6860 5G
- FRITZ!Box 6850 5G
- FRITZ!Box 6850 LTE
- FRITZ!Box 6690 Cable
- FRITZ!Box 6670 Cable
- FRITZ!Box 6660 Cable
- FRITZ!Box 6591 Cable
- FRITZ!Box 6590 Cable
- FRITZ!Box 6490 Cable
What is band steering and how does it work?
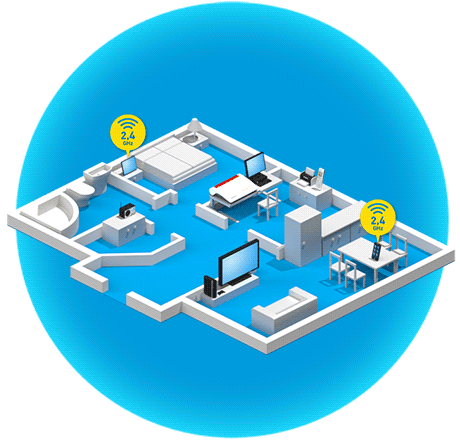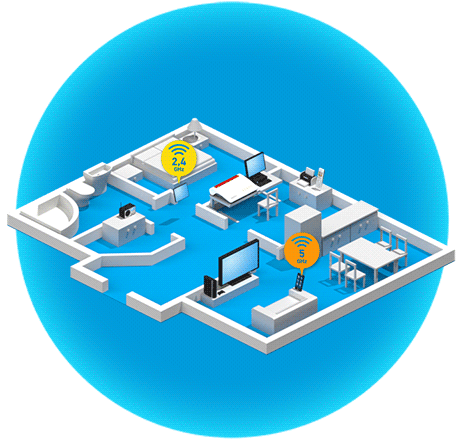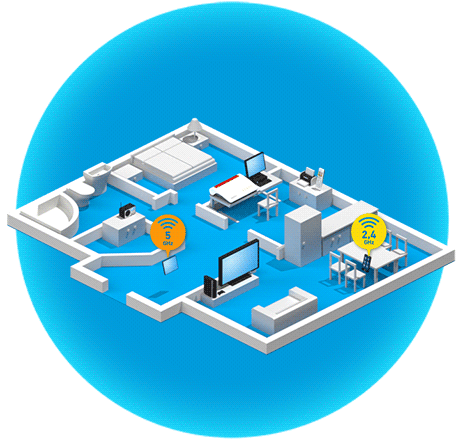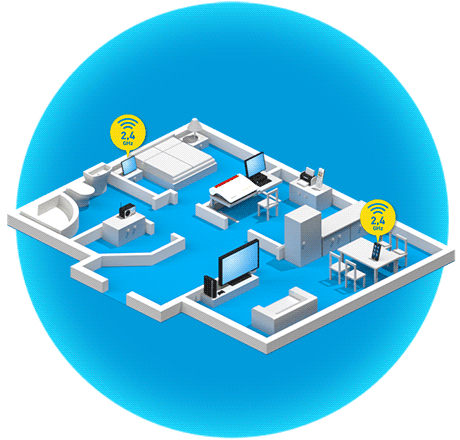
Wireless routers and wireless repeaters that make several Wi-Fi networks available, for example the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands, at the same time (for example FRITZ!Box 7590 AX, FRITZ!Repeater 2400) can use band steering to automatically steer wireless devices to the ideal Wi-Fi network. This way, band steering balances the load in the Wi-Fi network, which ensures fast and stable connections of all of the wireless devices in the home network.
Automatic steering to the optimal Wi-Fi network
Wireless devices that support connections to several Wi-Fi networks decide themselves which Wi-Fi network to connect to. However, wireless devices do not always make the best choice. With band steering, routers and repeaters can determine which Wi-Fi network is more suitable for individual wireless devices and automatically steer them to the more suitable one.
For example, the FRITZ!Box uses band steering to improve the range of wireless devices when they are connected to the 5 GHz Wi-Fi network and are on the edge of the range. The FRITZ!Box then initiates a switch to the 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi network which has a greater range.
Characteristics of the Wi-Fi networks
The 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi has a greater range because low frequencies can penetrate obstacles such as walls, metallic objects, or objects containing water more easily.
The 5 GHz Wi-Fi network offers more speed near a wireless router because it allows you to use a wider frequency spectrum, therefore allowing larger amounts of data to be transmitted in the same amount of time.
Requirements for band steering
Band steering is already enabled in the FRITZ!Box's factory settings. Together with AP steering, band steering forms the basis for Mesh Wi-Fi steering in the FRITZ! Mesh. However, band steering does not work if different names were configured in the FRITZ!Box for the Wi-Fi networks. In this case you must optimize the Wi-Fi network of the FRITZ!Box.
In order for the wireless devices to be steered by the FRITZ!Box, the devices must support the wireless standards 802.11k and 802.11v:
- The FRITZ!Box can seamlessly steer wireless devices that support the wireless standards 802.11k and 802.11v to the ideal Wi-Fi network.
- The FRITZ!Box can only steer older wireless devices that do not support the wireless standards 802.11k and 802.11v to a different Wi-Fi network by briefly clearing the Wi-Fi connection.
Note:The FRITZ!Box displays wireless devices that support the standards 802.11k and 802.11v under "Wi-Fi > Wi-Fi Network > Known Wireless Devices" ("Wireless > Radio Network > Known Wireless LAN Devices") with the properties "11k" und "11v".